Functions:
There are 2 Functions which are Aggregate and Scalar function. Aggregate function contains sum, count, average and Min/Max. Where as Scalar function has Ucase/Lcase, Length, Concat.
1) Aggregate Functions:
Aggregate functions calculate single value by performing
given operation on column.
Syntax:
select Sum(Column1) from Tablename;
Example:
select Sum(Salary) from Employee;
Syntax:
select Count(Column1) from Tablename;
Example:
select Count(ID) from Employee;
Syntax:
select Average(Column1) from Tablename;
Example:
select Average(Salary) from Employee;
Syntax:
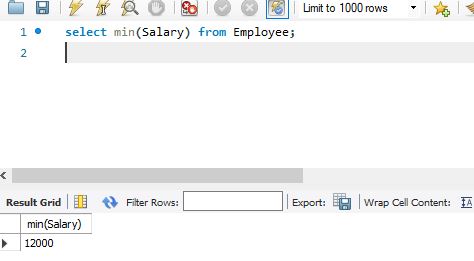
select Min(Column1) from Tablename;
select Max(Column1) from Tablename;
Example:
Select Min(Salary) from Employee;
Select Max(Salary) from Employee;
2) Scalar Functions:
Syntax:
select Ucase(Column1) from Tablename;
Example:
select Ucase(First_name) from Employee;
Syntax:
select length(Column1) from Tablename
Where column1 = value1;
Example:
select length(First_name) from Employee
where ID = 101;
Syntax:
select concat(value1', 'value2');
Example:
select concat('Raj', 'Marthur');
% - The percent sign represents zero, one, or multiple characters
_ - The underscore represents a single character
You can use Like operator with And, Or conditions
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename
Where Column1 like a%
Example:
Select * from Employee
Where First_name like a%
You can check every operator one by one.
Syntax:
Select column1, column2 as newname , column3
from Tablename;
Select * from tablename as newtablename;
Example:
Select ID, First_name as name, salary from
Employee;
Select * from Employee as Employeedetail;
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename
Where column1 between value1 and value2;
Example:
Select * from Employee
Where Salary between 12000 and 20000;
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename
Where column1 in (value1, value2);
Example:
Select * from Employee
Where Company in (Infosys, Capgemini);
Distinct: When you want to only select Distinct values and avoid all Duplicate values.
Syntax:
Select Distinct * from Tablename;
Example:
Select Distinct * from Temp1;
Union: Union is used When you only want to select unique values from two tables. This operation only get performed when Column names and datatype of both tables are same.
it is just like appending data but elimination duplicate values.
look at the Temp1 and Temp2 table carefully. you will see the difference in Union, Union all, intersect, except condition.
it is just like appending data but elimination duplicate values.
look at the Temp1 and Temp2 table carefully. you will see the difference in Union, Union all, intersect, except condition.
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename1
union
Select * from Tablename2;
union
Select * from Tablename2;
Example:
Select * from Temp1
union
Select * from Temp2;
union
Select * from Temp2;
Union All: Union all is used When you only want to append data and you don't care about duplicate data.
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename1
union all
Select * from Tablename2;
union all
Select * from Tablename2;
Example:
Select * from Temp1
union all
Select * from Temp2;
union all
Select * from Temp2;
Intersect : Intersect operation is not possible in MySQL but it works in MS SQL and others.
In intersect it will only take the common values from both tables. if there is duplicate value which is common then takes it only once.
In intersect it will only take the common values from both tables. if there is duplicate value which is common then takes it only once.
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename1
intersect
Select * from Tablename2;
intersect
Select * from Tablename2;
Example:
Select * from Temp1
intersect
Select * from Temp2;
intersect
Select * from Temp2;
Except : Except operation is also not possible in MySQL but it works in MS SQL and others.
In Except if You want A Except B then it will only give you values which are present in A but not in B. if you have written B except A then it will only provide you values present in B and not in A.
In Except if You want A Except B then it will only give you values which are present in A but not in B. if you have written B except A then it will only provide you values present in B and not in A.
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename1
Except
Select * from Tablename2;
Except
Select * from Tablename2;
Example:
Select * from Temp1
Except
Select * from Temp2;
Except
Select * from Temp2;
Top/Limit: Top/Limit is used to get Top n row of table and limit is use. You can put where condition to get required result. Top operation Does not work in MySQL you can use Limit instead.
Syntax:
Select Top 3 * from Tablename1;
Select * from Tablename1
limit 3;
limit 3;
Example:
Select Top 3 * from Employee;
Select * from Employee
limit 3;
limit 3;
Rownum: To select particular row from table according to row number.
Syntax:
Select * from Tablename1
Where Rownum = Value1;
Where Rownum = Value1;
Example:
Select * from Employee
Where Rownum = 2;
Where Rownum = 2;
Rownum operation is not supported in MySQL but it gives proper result in MS SQL and others.
















No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to ask us any question regarding this post